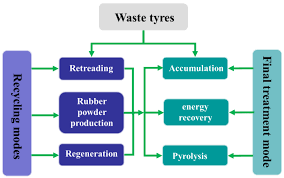
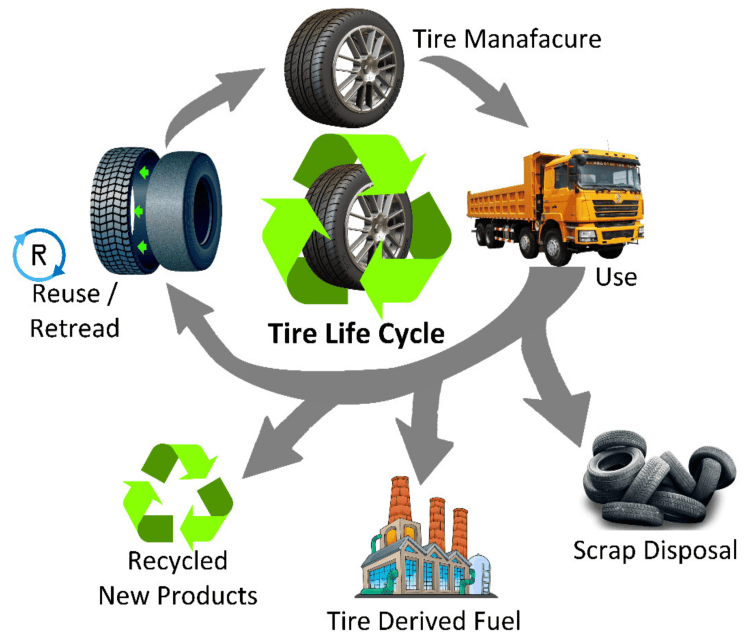
Introduction
In our rapidly evolving world, where sustainability is becoming more crucial than ever, paper recycling emerges as a critical player in the quest for environmental preservation. Paper, a ubiquitous commodity, forms the backbone of our daily lives, from office documents to packaging. However, its environmental impact can be significant if not managed properly. This blog explores the multifaceted ways in which paper recycling contributes to environmental conservation, examining its benefits, processes, challenges, and future prospects. By delving into these aspects, we will uncover how paper recycling is not just a waste management practice but a fundamental component of a sustainable future.
Waste: The Importance of Paper Recycling
Paper recycling is a process through which used paper products are collected, sorted, and converted into new paper products. This practice helps mitigate the environmental impact associated with paper production and waste. Understanding its significance involves looking at several critical factors:

1. Reduction in Waste
One of the most direct benefits of paper recycling is the reduction of waste. Paper accounts for a substantial portion of municipal solid waste. In the U.S., for example, paper and paperboard make up about 25% of all waste sent to landfills. By recycling paper, we divert this waste from landfills, reducing the strain on waste management systems and extending the lifespan of landfills.
2. Conservation of Resources
Producing paper from recycled materials requires fewer raw materials compared to making paper from virgin wood pulp. By recycling paper, we conserve natural resources such as trees, water, and energy. Each ton of recycled paper can save approximately 17 trees, 7,000 gallons of water, and 4,100 kilowatts of electricity.
3. Waste: Reduction in Pollution
Paper production from virgin materials involves several stages that generate pollutants, including air and water pollution. By recycling paper, we minimize the need for new raw materials, which in turn reduces emissions of harmful substances and decreases water and air pollution associated with paper manufacturing.
4. Waste: Energy Savings
The energy required to produce paper from recycled fibers is significantly lower than that needed to produce paper from virgin fibers. Recycling paper can save up to 40% of the energy required for new paper production. This reduction in energy consumption contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, which helps combat climate change.
Waste: The Paper Recycling Process
Understanding the environmental benefits of paper recycling requires a closer look at how the recycling process works. Here’s a detailed overview of the steps involved:

1. Collection and Sorting
The recycling process begins with the collection of used paper products. This is typically done through curbside pickup, drop-off centers, or commercial collection services. Once collected, the paper is transported to a recycling facility where it is sorted into different grades, such as newsprint, cardboard, and office paper.
2. Shredding and Pulping
After sorting, the paper is shredded into small pieces and mixed with water to create a slurry called pulp. This pulp is then processed to remove any contaminants, such as staples, labels, or glue, which can interfere with the recycling process.
3. Deinking
The next step involves removing ink and other impurities from the pulp. This is achieved through various methods, including flotation, which separates ink particles from the paper fibers. Deinking ensures that the recycled paper has a clean and uniform appearance.
4. Bleaching and Refining
Depending on the desired quality of the recycled paper, the pulp may undergo bleaching to achieve a whiter color. This step is often optional and depends on the end use of the paper. The pulp is then refined to improve its strength and consistency.
5. Papermaking
The cleaned and refined pulp is then spread onto screens to form a continuous sheet. This sheet is pressed to remove excess water and then dried to create paper. The dried paper is rolled into large reels and can be further processed into various products, such as newsprint, cardboard, and packaging materials.
6. Recycling into New Products
The final step involves converting the recycled paper into new products. These can range from new paper products like tissues and notebooks to packaging materials and cardboard boxes. The recycled paper fibers can be reused multiple times, although they gradually lose strength with each cycle.
Waste: Environmental Benefits of Paper Recycling
The environmental advantages of paper recycling are manifold, contributing to a more sustainable planet. Here’s an in-depth look at how recycling paper positively impacts the environment:

1. Preservation of Forests
Forests are vital ecosystems that support biodiversity, regulate climate, and provide resources for millions of people. By recycling paper, we reduce the demand for virgin wood pulp, thereby helping to preserve forests and combat deforestation. This preservation of forests also contributes to maintaining wildlife habitats and promoting ecological balance.
2. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Paper recycling plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The energy savings associated with recycling paper translate into lower carbon dioxide emissions. By reducing the need for new paper production, which is energy-intensive, recycling helps mitigate climate change and its associated impacts.
3. Conservation of Water Resources
The paper production process consumes large quantities of water, both for growing trees and for processing the wood into paper. By recycling paper, we conserve water resources by reducing the need for new paper production. This conservation is particularly important in regions experiencing water scarcity.
4. Decreased Pollution
Recycling paper results in lower emissions of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. It also reduces water pollution, as recycled paper production generates less wastewater compared to manufacturing paper from virgin fibers. This reduction in pollution benefits both human health and the environment.
5. Energy Efficiency
Recycling paper saves significant amounts of energy compared to producing paper from raw materials. This energy efficiency translates into lower reliance on fossil fuels and reduced greenhouse gas emissions
How Paper Recycling Helps the Environment
This blog explores the multifaceted ways in which paper recycling contributes to environmental conservation, examining its benefits, processes, challenges, and future prospects.
The Endless Benefits of Plastic Recycling
This blog explores comprehensively the multifaceted advantages of plastic recycling, ranging from environmental to economic and societal impacts.
The Importance of Plastic Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog explores the importance of plastic recycling, examining its benefits, challenges, innovations, and future prospects.